![]()
Chapter 6 Knowledge Representation
procedural knowledge
declerative knowledge -----------------------> new
declerative knowledge
(x,y) --> declerative knowledge
IF ( X ? 4) THEN FILL X TO X = 4 ---> procedural knowledge
An object which does not contain given details is a simple object.
An object which can be classified according to given details is a structured
object.
KR -----> knowledge formalized in a symbolic form
![]()
IF situation THEN action
IF days sales outstanding > 30 THEN check involving procedure.
IF antecedent THEN consequent
IF X is accounts payable THEN X belongs to curent liabilities.
conjunction (and) disjunction (or) of antecedents.
IF (company ALPHA, loan????? application, loan size $4,500)
THEN (company ALPHA, reject Loan)
-too small explanation
6.3 Knowledge Representation Methods
Elemantary unit in predicate calculus is an object. Statements about objects are called predicates. For example, is-blue(car) is an assertion that says that the cars is blue.
Predicate calculus describes a world which has the following form.
First-order Predicate Calculus ===>
Permits variables represent objects only.
Second-order Predicate Calculus ===> Permits variables represent
predicates (functions)
![]()
E.g.
| SLOTS | ENTRIES |
| Name of frame : | Toaster |
| Type of frame : | Toaster condition |
| Heating element : | Glows |
| Fuse : | OK |
| Thermostat : | Working order |
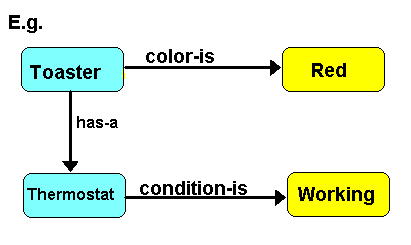
A semantic net is a collection of objects called nodes. The nodes are connected together by arcs or links. Both the links and nodes are labeled.
Nodes : used to represent objects and descriptions. (Descriptors provide additional info about objects.)
Links : relate objects and descriptors. Also represent relationships.
 .
.
![]()
6.3.4 Object-Attribute-Value(O-A-V) Triplets
Attributes are general characteristics or properties associated with objects.For example, interest rate is an attribute for a bank loan.
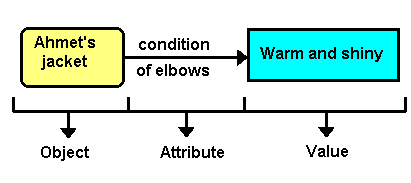
O-A-V and Semantic Networks
O-A-V is a specialized case of the semantic-net approach.
object
==> attribute "has
a"
attribute ?==
value
"is a"
The object ==> attribute link is a "has-a" link.
A bank has a rate of
interest.
The attribute ==>value links is a "is-a" link.
12% is a rate of interest.
![]()
Rules are used to represent relationships. Rule-based
knowledge representation employs
IF condition THEN action
statements.
(premise
(goal
antecedent)
consequent)
For example,
IF the heating element glows AND the bread is always dark
THEN the toaster thermostat is broken
When the problem situation matches th IF part
of a rule, the action specified by the THEN part of the rule is performed.
![]()
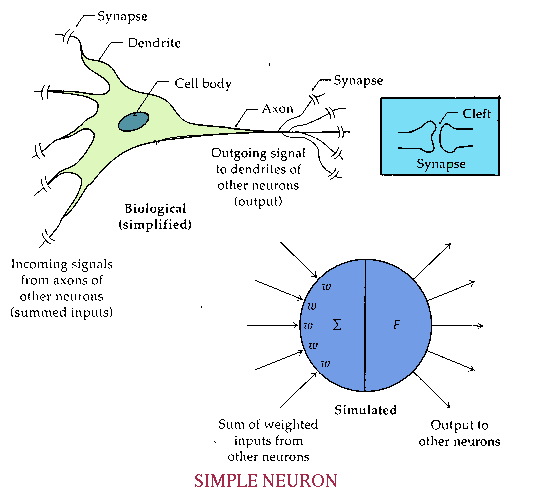
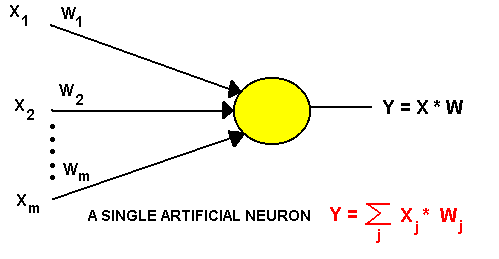
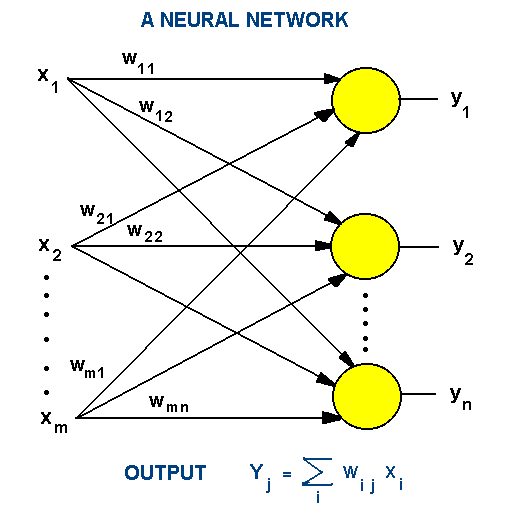
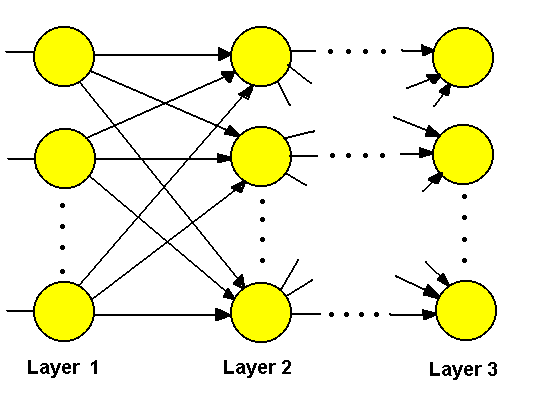
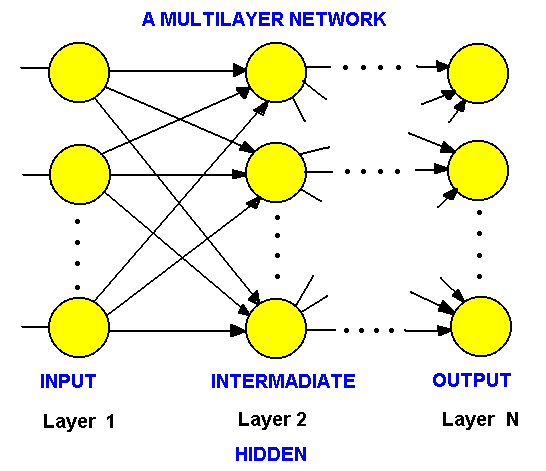
6.3.6 Neural
Networks
Knowledge representation using Neural Networks :